[ad_1]
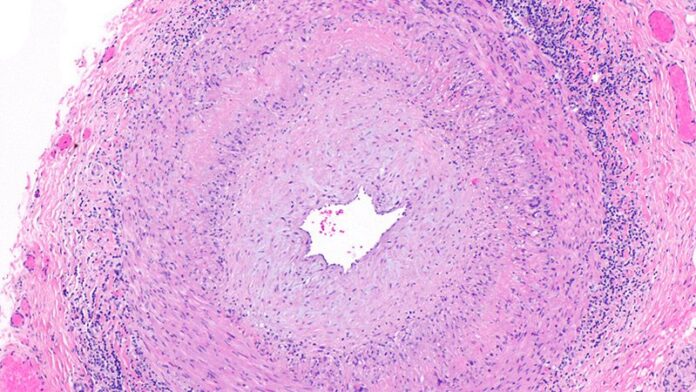
Positive findings from frozen sections of a first temporal artery biopsy can effectively identify giant cell arteritis, ruling out in those cases the need to perform a second biopsy on the contralateral side and arguing against the use of simultaneous bilateral biopsies, according to results from a retrospective study of nearly 800 patients who underwent the procedure at the Mayo Clinic during 2010-2018.
Although temporal artery biopsy (TAB) remains the standard diagnostic test for giant cell arteritis (GCA), second TAB procedures are often performed in patients with a high level of suspicion for GCA, which may result in unnecessary treatments and complications, Devon A. Cohen, MD, of the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., and colleagues wrote. (Cohen is now a clinical fellow in ophthalmology at the Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary.)
At the Mayo Clinic, TAB specimens are first examined with frozen sections at the time of the biopsy; this process, followed within days by formalin-fixed tissue permanent sections, is unique to Mayo. “A frozen section–guided sequential TAB is commonly performed, with the results of the first biopsy obtained within minutes, which determines the need for evaluation of the contralateral side,” the researchers said. However, the use of frozen sections to evaluate patients with GCA has not been well studied.
In a retrospective cohort study published in JAMA Ophthalmology, the researchers identified TAB patients aged 40 years and older who underwent TAB procedures between Jan. 1, 2010, and Dec. 1, 2018, at the Mayo Clinic. The average age of the patients was 72 years, and 41% were men.
Table of Contents
Strong Positive Predictions From Frozen Sections
The researchers analyzed 1,162 TABs from 795 patients using frozen and permanent histologic sections.
Overall, 119 patients (15.0%) and 138 TABs had positive permanent section findings, and 103 (86.6%) of these patients also had positive frozen section findings, including 4 false positives and 20 false negatives. The frozen section specificity and sensitivity was 99.4% and 83.2%, respectively, for detecting inflammation suggestive of GCA, and the positive and negative predictive values were 96.1% and 96.6%, respectively. Positive and negative likelihood ratios for frozen section were 140.6 and 0.17, respectively.
In a multivariate analysis, the odds of a positive permanent section TAB significantly increased with age (odds ratio, 1.04), vision loss (OR, 2.72), diplopia (OR, 3.33), headache (OR, 2.32), weight loss (OR, 2.37), and anorexia (OR, 5.65).
A total of 60 patients underwent bilateral TABs, and 307 patients underwent bilateral frozen section–guided sequential TABs; the discordance rates based on permanent sections were 5.0% and 5.5%, respectively.
Those discordance rates are “an important result applying to everyone working with patients suspected for GCA,” Patricia Chévez-Barrios, MD, of Houston Methodist Hospital, wrote in an accompanying editorial. “This is on the low end of what was previously published (3%-40%) and supports the relative low need for bilateral synchronous TAB for the diagnosis of GCA.”
A key issue in GCA diagnosis is the need to confirm inflammation, Chévez-Barrios said. “The surgeon must obtain a significant portion of the artery, and the pathologist should review several sections and levels of the tissue to confidently say whether there is inflammation or no.”
Frozen Sections Can Spare Patients From Second Procedures
The findings suggest a role for frozen section to help to determine whether a unilateral or bilateral simultaneous TAB should be performed, the study authors noted.
“If the frozen section is positive on the first TAB, a contralateral TAB is deferred, given the very low false-positive rate (0.6%). However, if the frozen section does not align with the permanent section result, in particular if the frozen section is positive but permanent section is negative, the patient returns for a TAB on the contralateral side if the GCA suspicion remains high,” they said.
The use of frozen sections requires ideal conditions in order to be effective, Chévez-Barrios said. The Mayo Clinic approach “is only possible because of their appropriate hospital setting, the training of the histotechnologists, and the experience of the pathologists interpreting the stains and sections. For most pathology laboratories outside of the Mayo Clinic, frozen sections on arteries are the exception and are used only in specific scenarios.”
In addition, the American College of Rheumatology recommends that patients with a high suspicion of GCA should begin corticosteroids as soon as laboratory studies are obtained; “As a result, if a TAB is performed after treatment begins, the typical active pattern of inflammation in the artery changes,” Chévez-Barrios said. “This further challenges the diagnosis in a frozen section setting because of the need for immunohistochemistry.” Although frozen sections are feasible in specialized settings such as the Mayo Clinic, most patients receive adequate diagnosis and treatment based on permanent sections.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the use of data from patients at a single center and the unique setup of the Mayo Clinic to perform rapid processing of frozen sections, the researchers noted.
“Additionally, we acknowledge that there is controversy regarding the clinical interpretation of healed arteritis. At our institution, healed arteritis is interpreted in the context of patient clinical characteristics and radiographic findings, which may differ from other institutions and may impact the results of this study,” they said.
Overall, the results support the potential of frozen sections in guiding TAB, although “more studies with a comparative analysis of laboratory results, clinical symptoms, and patient demographic characteristics between positive and negative frozen and permanent TAB results are needed to confirm our findings,” they concluded.
The study received no outside funding. One author reported receiving grants from Eli Lilly and Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals as well as personal fees from Genentech-Roche and Sanofi. Chévez-Barrios had no financial conflicts to disclose.
This article originally appeared on MDedge.com, part of the Medscape Professional Network.
[ad_2]
Source link